You can create a DSL dictionary file in any text editor. We recommend using Notepad for the purpose.
- Create a new text file in Notepad or any other text editor. At the
very beginning of the new text document, enter the header for the new
dictionary. You can copy the header from this example and then paste
it into your document:
#NAME “My first dictionary”
The codes #NAME, #INDEX_LANGUAGE, and #CONTENTS_LANGUAGE must begin a new line each. These codes are followed by one blank space and some text in inverted commas. This text must be provided by the user and means the following. “My first dictionary” is the name of your new dictionary, “English” is the source language of your new dictionary, and “Russian” is its target language.
#INDEX_LANGUAGE “English”
#CONTENTS_LANGUAGE “Russian”
- Now write the text of your new dictionary card. Every dictionary card must have a headword and body. A headword is a word or expression to be translated. It must always be placed at the start
of a line (i.e. there must be no other characters or spaces on this
line preceding the headword). The body of the card contain a
translation, comments, notes or any other information you may wish to
include. The body of the card must be placed below the headword and be
preceded with a blank space (inserted by pressing the Space button) or a tabulation symbol (inserted by pressing the TAB key). This will enable ABBYY Lingvo x3 to distinguish the headword from the body text.
To see how it works, simply copy the sample text given below into your document below the header:
my first dictionary
мой первый словарь - Save the dictionary file in Unicode encoding (in the Save As… dialog box, select Unicode in the Encoding drop-down list) and name the file FirstDictionary. Close Notepad or any other text editor you may have used.
- Change the extension of the text file to .dsl – for example, in Windows Explorer. (If you do not see the extension of the file, in Windows Explorer, go to Tools>Folder Options, click the View tab and clear the box next to “Hide extensions for known file types”.)
- Launch DSL Compiler (Start>All Programs>ABBYY Lingvo x3>DSL Compiler x3).
- In the DSL Compiler dialog box that opens, under the Source file properties group, browse to the file FirstDictionary.dsl, which contains the dictionary you created and select the Unicode option below.
Make sure that the Create dictionary ready for indexing option is selected. With this option selected, DSL Compiler will automatically add the necessary markup to the dictionary (otherwise, this markup must be added manually by the user when creating the text file). Also make sure that the Create error log file (*.dde) option is selected. - Click Compile. If the compilation is successful, the About Dictionary
dialog box will open saying that the dictionary has been created
successfully. Two files will be created as a result of compilation: a
dictionary file called FirstDictionary.lsd and a file called FirstDictionary.dde which logs any errors detected during the compilation.
What shall I do if during the compilation I receive the massage saying that the annotation file was not found?
Annotation files are optional. They contain general information about a dictionary – its author, number of entries, etc. Our sample dictionary will have no annotation, so just click Yes in the message box that opens and the compilation process will continue.What shall I do if the program fails to compile the dictionary?
Compilation may fail due to errors in the file. See the list of errors in FirstDictionary.dde. Correct the errors and repeat the compilation process. - Add the dictionary to ABBYY Lingvo x3 (Tools>Add Dictionary from File…) or simply drag and drop the *.lsd file onto the ABBYY Lingvo x3 Bookshelf).
If you compare this sample dictionary with any of the dictionaries supplied with ABBYY Lingvo x3, you will notice that the sample card is much less informative: it includes no pronunciation, examples, comments, etc. However, the DSL language allows you to create dictionaries whose appearance and capabilities are similar to the ABBYY Lingvo dictionaries.
In your new dictionaries you can:
- highlight fragments of text in colour, change fonts to bold, italics or underlined by using special DSL tags
- mark different zones in dictionary cards
- add links to other dictionary cards and links to Web sites
- create an icon to be displayed on the ABBYY Lingvo x3 Bookshelf
- add pictures and sound to dictionary cards
- and much more…
http://www.LingvoDA.ru/ – The Web site of the Lingvo Dictionary Association offering a vast collection of free additional dictionaries for ABBYY Lingvo.
How can I create a dictionary in a different text editor, for example, Microsoft Word?
How can I expand and edit DSL dictionaries?
You can use any text editor, including Microsoft Word, to create the
text file of a new dictionary. Just make sure that the text complies
with the above requirements, i.e. contains a header which specifies the
name of your dictionary and its source and target languages, the
headword is placed immediately at the beginning of the line and the
body text below is preceded with a blank space or tab character. Once
you have typed the dictionary text, you need to save it in TXT format
with Unicode encoding. To do this:
- in Microsoft Word 2000, in the Save As dialog box, select Coded text in the Save As Type drop-down list.
- in Microsoft Word 2002, in the Save As dialog box, select Plain Text (*.txt) in the Save As Type drop-down list, then click Save. In the dialog box that opens, select Unicode in the Other Encoding list.
To add new cards or edit a dictionary which has already been
compiled and added to ABBYY Lingvo x3, remove the dictionary from ABBYY
Lingvo x3 Bookshelf, open the *.dsl dictionary file which
corresponds to the compiled *.lsd file and make the necessary changes.
Then recompile the dictionary and add it to the ABBYY Lingvo x3
Bookshelf.
New cards can also be created in a separate file which can then be attached to the main dictionary file with the help of the #INCLUDE command.
How can I create a dictionary annotation?
Annotations contain general information about dictionaries (i.e.
their author, subject, date of creation, etc.). This information can be
viewed in ABBYY Lingvo x3 by double-clicking the dictionary icon on
the Bookshelf. We recommend using Notepad to create annotation
files. The name of the annotation file must be the same as the name of
the dictionary it refers to. Save the file in Unicode, and then change the extension of the file to .ann. During compilation, this file will be used by DSL Compiler to add an annotation for your dictionary.New cards can also be created in a separate file which can then be attached to the main dictionary file with the help of the #INCLUDE command.
DSL Dictionary Structure
The source text of a DSL dictionary is a plain text file (*.txt), either in UNICODE or in ANSI encoding.
A DSL dictionary is made up of dictionary entries. An entry (card) has a headword (this can be a word or a phrase) and a body, which contains translations and comments. If a dictionary is added to the ABBYY Lingvo x3 Bookshelf, all of its card headwords are displayed in the word list. Clicking a word or phrase in the word list, opens the dictionary card which displays the corresponding entry.
ABBYY Lingvo x3 Multilingual supports dictionaries not only in Russian but also in other European languages (for the full list of supported languages, see the Supported Languages section). The source and target languages of the dictionary must be specified in the DSL file. Therefore, at the beginning of each DSL file you need to specify the name of your dictionary (#NAME “dictionary name”), its source language (#INDEX_LANGUAGE “language name”) and its target language (#CONTENTS_LANGUAGE “language name”).
E.g.: If you wish to create an English-Russian dictionary named “General”, type the following at the beginning of the DSL file:
#NAME “General”
#INDEX_LANGUAGE “English”
#CONTENTS_LANGUAGE “Russian”
If your dictionary consists of several files, use the #INCLUDE command to merge the files into one dictionary. Specify the full path to the file after a space or tabulation character. In the DSL language the back slash character “\” indicates that the character following it is text rather than a tag, so you have to use double slashes “\\” in the path to the file.
E.g.:
#INCLUDE “C:\\Dictionaries\\UniverseE.dsl”
Additionally, you can specify paths relative to the folder where the main DSL file (i.e. the file containing the #INCLUDE command) is located. In this case specify either the file name without the path or put a full stop (“.”) at the beginning of the path.
E.g.:
- If the initial dictionary is in Dictionaries, the dictionary to be merged (Universe2.dsl) is in the same folder:
#INCLUDE “Universe2.dsl”
- If the initial dictionary is in Dictionaries, the dictionary to be merged (Universe2.dsl) is in the Dictionaries\Dic folder:
#INCLUDE “Dic\\Universe2.dsl”
- If the initial dictionary is in Dictionaries\Dic, the dictionary to be merged (Universe2.dsl) is in the Dictionaries folder:
#INCLUDE “..\\Universe2.dsl”
- If the dictionary text was typed in ANSI encoding, you must specify
the code page for the source text, i.e. add a code page tag after the
target language and source language tags:
#SOURCE_CODE_PAGE “code page name”.
Allowed code page names:
Allowed code page name Windows code page number Latin 1252 Cyrillic 1251 EasternEuropean 1250 - If you save the text of the dictionary in ANSI encoding, make sure that the dictionary source and target languages are supported by the same code page. If there is no such code page, save the dictionary in UNICODE.
- If you save the text of the dictionary in UNICODE, you don’t have to specify the code page.
DSL Card Structure
A DSL card has the following structure: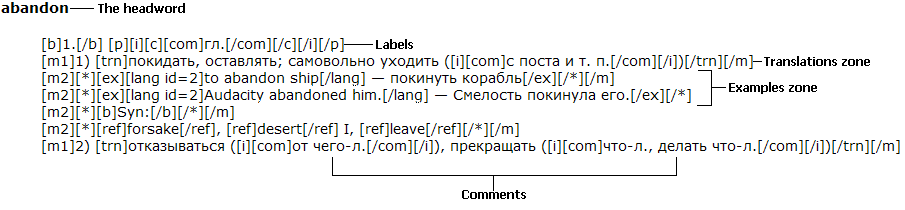
- The headword
The headword must be typed starting from the first position of a new
line. Allowed characters: letters of alphabets, numbers, spaces,
hyphens, commas and braces {} – to mark the unsorted part of the headword.
- The card body
The body of the card follows the headword and starts on a new line.
The first character in each line of the body must be either a space (or
several spaces) or a tab (or several tabs). The card body ends at the
next headword, which starts a new line. The card body may end at the
end of the file.
- labels (optional)
- translations zone
- comments zone (optional)
- examples zone (optional)
- pictures or sound (optional)
- links to Web pages (optional)
You can insert one or several blank lines between the body of one card and the headword of the next card to make the source text more readable. Entries in the source text need not be arranged in alphabetical order. You cannot have two entries with the same headword. However, capitalization matters and “Cardigan” and “cardigan” are considered as two different headwords.
How Entries Are Sorted
The headword of a card can be either a word or a phrase. The words in the headword can be separated by any number of spaces. However, multiple spaces will be substituted by one space when the card is displayed in ABBYY Lingvo x3. Spaces are taken into account when headwords are arranged alphabetically in the word list.One card may have several headwords. If you want a card to have several headwords, first type these headwords (each starting a new line), and then type the body text of the card. All the headwords will be shown in the word list (each headword in its own place in the list). Clicking any of the headwords will open the corresponding card.
The word list can contain words in different languages; these may be headwords of entries or headwords of subentries. Words in each of the languages are arranged in their “natural” dictionary order (i.e. alphabetically); Cyrillic letters follow Latin letters.
Characters that are not ignored
Hyphens (-), full stops (.), underscore (_), comma (,), and forward slash (/) are not ignored.
You can use parentheses to mark an optional part of the headword and curved braces to mark an unsorted part of the headword.
You can use any special symbols (like ~ or ^) in the headword text, but you must put a backslash (\) before each of such symbols. To use a backslash itself in the headword text, you must put double backslash (\\).
Unsorted Part of an Entry Headword
An entry headword can have an unsorted part. The unsorted part serves to include in the headword certain linguistic information which helps to understand how to use the headword (i.e. what words the headword is usually used with, government model examples etc.) yet, if it were sorted, affects the position of the headword in the word list in an undesirable way.The unsorted part is not displayed in the ABBYY Lingvo x3 word list and is not used for translation. This means that when you add an unsorted part to an entry headword you do not create a new headword, and so you cannot use the tilde to denote both the headword and the unsorted part you added.
The unsorted part is displayed on the screen only in the entry headword. You should use braces to select a part of the dictionary text as the unsorted part of an entry headword. Example:
{to }have
иметь
Additionally, braces can be used in the headword or the body of the card to mark superscript or subscript.
for example, CO{[sub]}2{[/sub]}-Laser
Optional Part of an Entry Headword
A card headword can have an optional section marked by brackets.You can use parentheses to provide spelling variants for a word, or to show that a certain morphological feature present in the source language is irrelevant in the target language.
E.g.:
превращать(ся)
turn into
This is equivalent to the following:
превращать превращаться
turn into
However, in the first case “превращать(ся)” will be displayed as the headword of the card.
If you have marked several headword sections as non-obligatory, the overall word list will contain every possible variant of the headword. For example, a headword written as follows: (пре)вращать(ся) will be displayed in the overall word list in four variants: превращаться, превращать, вращаться and вращать.
Note.We recommend that you do not use parentheses in headwords for any purpose other than described above.
Subentry
A card (entry) may have a subentry. Subentries are usually used to list common expressions and phrases in which the headword is used. Like a card, a subentry has a headword and a body. When ABBYY Lingvo x3 displays a main card, only the headwords of its subentries are displayed in it. Subentries are highlighted in a different colour. When you click a headword of a subentry, the corresponding card is displayed. Headwords of subentries are displayed in the word list; clicking them will display the corresponding cards. When you select a word combination in an external application and press CTRL+C+C or CTRL+INSERT+INSERT, the corresponding subentry card (if any) will also be displayed. One card (entry) may have several subentries.The headword of a subentry must start a new line, the first position in the line must be a space or tab, followed by @. The body of a subentry has the same structure as the body of a card, but must end with @ placed on the next line. The following example shows a card with two subentries, one of which refers to meaning 1), and the other to meaning 3):
Example 1:
little
1) маленький
[m1][*]
@ little one
малыш
@
[/*][/m]
2) немного, мало
3) пустяк, мелочь
[m1][*]
@ little by little
мало-помалу, постепенно
@
[/*][/m]
The headword of a subentry headword may have an alternative and/or an unsorted part. These parts are only displayed in the mother card. The headword of a subentry displayed in the mother card is a hyperlink to the subentry card. Clicking this hyperlink will open the subentry card.
In ABBYY Lingvo x3 system dictionaries, all subentries are displayed only in full translation mode, as they are enclosed in [*] and [/*] tags. If you want your user dictionary to look like a ABBYY Lingvo x3 system dictionary, enclose subentries in [*] and [/*].
Example 2:
little
1) маленький
[m1][*] @ little finger
мизинец
@ little ways
маленькие, смешные слабости
@
[/*][/m]
Note. If a card contains several subentries in a row, as in example 2 above, the beginning of a new subentry serves as the end of the previous subentry (you can put only one @ sign to separate two subentries).
Using the Tilde
As you have noted, we retyped the headword whenever we needed it in the card text of the previous section examples. There is a way to avoid such retyping, and that’s the tilde use. If you type a tilde (~) in any card part (for example, in a subentry header), this tilde will be replaced with the entry headword when displaying the card text or subentry card. NB: If there is more than one headword in a card, the first one will be used to replace the tilde. See the following example: the card “binary” can be written as follows:binary
бинарный
@ ~ search tree
бинарное дерево поиска
@ ~ search
бинарный поиск
@
You can use tilde in the text of a single card as many times as you want. You can even use multiple tildes in a single subentry headword (for example, you can have the following subentry – ~ in ~ – in the “all” card, equivalent to “all in all”).
A tilde used in the subentry text is replaced with the card, not subentry header.
If a card headword contains an unsorted part (or parts), any tilde used in the card text will be replaced with the longest sorted part of the entry headword.
A ^ sign typed before a tilde changes the case of the first letter of the word the tilde is to be replaced with – if the first letter were capital, it’ll become small, and vice versa. See the following example:
Havana
Гавана, столица Кубы
@ ^~
гаванская сигара
@
Links to Another Card
Linking to other cardsA card or subentry (subcard) can contain a link to another card (for example, a synonym or antonym). To create a hyperlink, you should type one of the headwords of the card referenced to in the body of your card enclosing it in broken brackets. A word in broken brackets may be placed in any part of the card but in subentry headword; you aren’t obliged to put it in the beginning of a line. When it comes to displaying a card, a link isn’t marked with any specific sign but displayed in the same colour as subentry headword. When you click it another card with the word’s translation opens.
For example, the following card contains a link to the word “binary”:
data
данные, см. также <<binary>>
If you create a link to a card, the headword of which contains an unsorted part, you can refer to any of the respective headword variants. In any case, the unsorted part of the headword must be suppressed.
Inserting a link to a card from another dictionary
- To insert a link to a card from another dictionary, use the [ref] tag. Use the name of the desired dictionary as the tag’s parameter.
- The name of the dictionary should be enclosed in quotation marks and preceded by the “dict” suffix.
- If the parameter is not specified, the link will point to a card from the same dictionary that contains the card with the link.
- The [ref] tag should be closed by [/ref].
For example:
[ref dict="Another dictionary (En-Ru)"]some word[/ref]
Note. When using the [ref] and [/ref] tags, make sure that the card you refer to actually exists, as DSL Compiler will not automatically check the validity of such references
Comments
You can add comments to the source text of the dictionary. These comments will be ignored by the compiler. Any DSL tags present in the comments will also be ignored. Comments must be enclosed in double braces and may include several lines of text.{{An example of a card with two headwords}}
sale price
selling price
отпускная цена
A comment may begin anywhere on the line. Comments must not break up the headword of an entry or subentry. (However, you can add comments in the same line after the headword.) If you type a comment at the beginning of a line, you cannot type the card headword in the same line. However, you can type a subentry headword after the comment in this line.
Embedded comments are not allowed (i.e., you cannot enter a comment inside another comment).
Inserting Pictures and Sounds
You can insert a picture, sound or video file in a DSL dictionary entry (card). When you open the entry, the picture, sound or video file will be replaced with an icon. Click the icon to display the picture in a separate window, to listen to the sound or to see the video clip.Note.
- Multimedia files must be located in the folder of the corresponding dictionary.
- If the image, sound or video files are added when compiling the dictionary, these files need not be located in the folder where the dictionary itself is located.
- Write the name of the image file followed by the multimedia tags.
Supported image formats:
BMP, Bitmaps (*.bmp)
PCX (*.pcx)
DCX (*.dcx)
JPEG (*.jpg)
TIFF (*.tif)
To insert a sound in a DSL dictionary entry:
- Write the name of the sound file followed by the multimedia tags.
Note. A sound card compatible with your operating system should be used for listening sound files.
Supported sound formats:
Wave Sound (*.wav)
To insert a video in a DSL dictionary entry:
- In the DSL text of your card, write the name of the video file followed by [s] tags.
Ex: [s]movie.avi[/s].
Inserting Internet Links
To insert a link to a Web page:- Write the address of the Web page followed by the [url], [/url] tags.
The link in the card is underlined and marked with colour (the same as the colour of links to other cards). You can change the colour on the Entry window view tab of the Options dialog box (Tools>Options…).
Click the link to open the Web page in the default browser.
Paragraph Formatting
When displaying a card text ABBYY Lingvo x3 formats each paragraph according to card window width. Paragraph margins are defined as follows:- each line is one paragraph
- subentry mark “@” is the beginning of a paragraph
You should specify the left paragraph margin (counted from the left card window margin) using the [m] tag (where N is any number from 1 to 9). Any paragraph from this tag until the end of card or until system meets an “[/m]” (margin shift toggle off) tag, will be displayed positioned N spaces to the right from the left card window margin.
For example, if you want to display the translation shifted by one space to the right from the card header, you should format the card as follows:
little
[m1]1) маленький[/m]
[m1][*]@ little one
малыш
@
[/*][/m]
[m1]2) немного, мало[/m]
[m1]3) пустяк, мелочь[/m]
[m1][*]@ little by little
мало-помалу, постепенно
@
[/*][/m]
Text Formatting
The new DSL version features special text formatting tools called formatting tags. Any formatting tool has two commands: toggle on tag and toggle off tag. Depending on this, the text entered between these tags will be formatted in a certain manner.Any toggle on tags look like [a], where a is a formatting tool tag (comprising either on or two characters). The respective toggle off tag looks like [/a].
Implemented are the following text formatting tools:
- boldfaced text ([b] tag)
- italics ([i] tag)
- underlined text ([u] tag)
- coloured text ([c] tag; available colours: Aliceblue,
antiquewhite, aqua, aquamarine, azure, beige, bisque, blanchedalmond,
blue, blueviolet, brown, burlywood, cadetblue, chartreuse, chocolate,
coral, cornflowerblue, cornsilk, crimson, cyan, darkblue, darkcyan,
darkgoldenrod, darkgray, darkgreen, darkkhaki, darkmagenta,
darkolivegreen, darkorange, darkorchid, darkred, darksalmon,
darkseagreen, darkslateblue, darkslategray, darkturquoise, darkviolet,
deeppink, deepskyblue, dimgray, dodgerblue, firebrick, floralwhite,
forestgreen, fuchsia, gainsboro, ghostwhite, gold, goldenrod, gray,
green, greenyellow, honeydew, hotpink, indianred, indigo, ivory, khaki,
lavender, lavenderblush, lawngreen, lemonchiffon, lightblue,
lightcoral, lightcyan, lightgoldenrodyellow, lightgreen, lightgrey,
lightpink, lightsalmon, lightseagreen, lightskyblue, lightslategray,
lightsteelblue, lightyellow, lime, limegreen, linen, magenta, maroon,
mediumaquamarine, mediumblue, mediumorchid, mediumpurple,
mediumseagreen, mediumslateblue, mediumspringgreen, mediumturquoise,
mediumvioletred, midnightblue, mintcream, mistyrose, moccasin,
navajowhite, navy, oldlace, olive, olivedrab, orange, orangered,
orchid, palegoldenrod, palegreen, paleturquoise, palevioletred,
papayawhip, peachpuff, peru, pink, plum, powderblue, purple, red,
rosybrown, royalblue, saddlebrown, salmon, sandybrown, seagreen,
seashell, sienna, silver, skyblue, slateblue, slategray, snow,
springgreen, steelblue, tan, teal, thistle, tomato, turquoise, violet,
wheat, white, whitesmoke, yellow, yellowgreen, - colours supported by Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.0 or higher.
A colour name is not enclosed in quotation marks. If a colour name is not specified, the colour specified in ABBYY Lingvo x3 settings as the label colour is used, e.g.: [c],[c green]. If the tag is not used the text will be displayed in black. Examples and hyperlinks are exceptions to this rule. They have colours specified in the ABBYY Lingvo x3 settings.
selling price
[u][i]отпускная[/i] [b]цена[/b][/u]
Mind the fact that spaces before, after and in the middle of tags are present only if actually intended to be displayed. That means that you can format, if you want, only a part of the word (a single letter, the first and the last letters, etc.). If there is a space before and after a tag, only one space will be actually displayed.
The formatting tags must not overlap. If you toggled one formatting tag before another, you must toggle it off after the latter.
DSL Tags
All DSL tags have the following format: [a] (opening tag) or [/a] (closing tag).[b], [/b] – boldfaced font
[i], [/i] – italics
[u], [/u] – underlined font
[c], [/c] – coloured (highlighted) font
[*], [/*] – the text between these tags is only displayed in full translation mode (see)
[m] – sets the left paragraph margin. N is the number of spaces which will be used for the left-hand margin. N must be within the range from 0 to 9. The corresponding closing tag of the paragraph is [/m]. and left card margin.
[trn], [/trn] – translations zone.
[ex], [/ex] – examples zone.
[com], [/com] – comments zone.
[s],[/s] – multimedia zone (used to add pictures or sound files into a dictionary entries ).
[url],[/url] – link to a Web page.
[!trs], [/!trs] – the text between these tags will not be indexed
[p], [/p] – labels (clicking a label displays its full text)
['],[/'] – a stressed vowel in a word. You can change the colour of stressed vowels on the Entry window view tab of the Options dialog box (Tools>Options…).
[lang][/lang] – the language of the word or phrase; these tags are used in cards to mark words that are written in a language other than the target language. Words marked by [lang] tags will be indexed, translated, you will be able to see the list of their grammatical forms, etc. The name of the language must be enclosed in quotation marks, e.g. [lang name="Russian"]. See the list of supported DSL languages in the “Supported Languages” section.
[ref][/ref] – hyperlink to a card in the same dictionary (You can also use “<<” and “>>” to enclose the headword of the card to make a link).
Note. When using the [ref] and [/ref] tags, make sure that the card you refer to actually exists, as DSL Compiler will not automatically check the validity of such references.[sub][/sub] – subscript
[sup][/sup] - superscript
Marking of Zones for Full-Text Search
Once you have added a dictionary onto the Bookshelf, you need to index it in order to be able to carry out full-text searches in this dictionary. Click Update Index… in the Dictionaries dialog box to update the index. If you choose not to update the index upon adding the dictionary, the index will be automatically updated when you carry out your first full-text search in the newly added dictionary. User dictionaries are indexed in the same way as system dictionaries.Note. Index files are stored on the hard disk in the same folder where the dictionary is stored. Make sure that your have write permissions for this folder (for more information on working with indexes, see the Adding User Dictionaries to the Bookshelf section).To enable ABBYY Lingvo x3 to carry out full-text searches in the body text of the cards, you must enclose the text in special tags. Otherwise, ABBYY Lingvo x3 will only look for headwords.
If the structure of your dictionary entries is relatively simple (i.e. they consist merely of a headword followed by some text), you can automatically add [trn] and [/trn] tags to your cards to be able to carry out full-text searches in the dictionary. To do this, select the Create dictionary ready for indexing option in DSL Compiler. In this case, DSL Compiler will place a [trn] tag at the beginning of each card and a [/trn] tag at the end of each card. The syntax of the DSL language prohibits embedding zones of the same type, so before compiling your dictionary make sure that there are no [trn] tags in the entries. DSL Compiler will report a compilation error for each entry with embedded [trn] tags.
If your dictionary entries are complex and have several zones, you need to use special DSL tags to mark these zones:
- Use the [trn] and [/trn] tags to mark the translations zone. This zone will contain translations of the headword.
- Use the [ex] and [/ex] tags to mark the examples zone. This zone will contain usage examples.
- Use the [com] and [/com] tags to mark the comments zone. This zone will provide additional information about the translations.
- Use the [!trs] and [/!trs] tags to mark text fragments that must not be indexed (i.e. fragments you wish to be excluded from full-text search).
Compiling a Dictionary
To compile a *.dsl dictionary:- Click Start and select Programs>ABBYY Lingvo x3>DSL Compiler.
- In the DSL Compiler dialog box that opens, select the *.dsl file that contains the text of your dictionary and then select the required compilation parameters.
-
Note. If you wish image or sound files to be added to
the dictionary, place these files into the folder where the source DSL
file is located.
- Click the Compile button.
- The result of the compilation is a *.dde file and an *.lsd file. Correct the errors and warnings listed in the *.dde file (if any) and recompile your dictionary.
If your cards contain not only text in the target language, but also text fragments in other languages, you must enclose such fragments in lang tags.
If your dictionary consists of several files, use the #INCLUDE command to join the files during compilation.
Note.
- Starting from ABBYY Lingvo 9.0 you can convert *.lud dictionaries into *.dsl format.
- If you want your dictionary to be represented by its own icon on the Bookshelf, you need to create a 14×21 *.bmp image. The name of the image must be the same as the name of the dictionary file.
Sample Entries in DSL
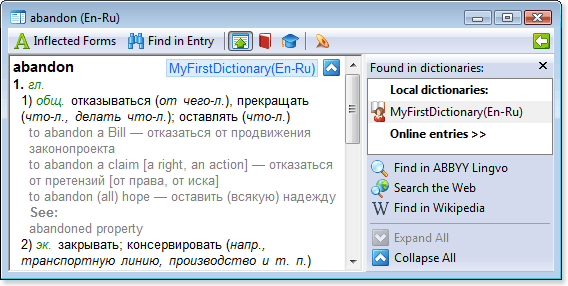
abandon[b]1.[/b] [p]гл.[/p]
[m1]1) [p][trn]общ.[/p] отказываться [com]([i]от чего-л.[/i])[/com], прекращать [com]([i]что-л., делать что-л.[/i])[/com]; оставлять [com]([i]что-л.[/i])[/com][/trn][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=1033]to abandon a Bill[/lang] — отказаться от продвижения законопроекта[/ex][/*][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=1033]to abandon a claim \[a right, an action\][/lang] — отказаться от претензий \[от права, от иска\][/ex][/*][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=1033]to abandon (all) hope[/lang] — оставить (всякую) надежду[/ex][/*][/m]
[m2][*][b]See:[/b][/*][/m]
[m2][*][com][lang id=1033]abandoned property[/lang][/com][/*][/m]
[m1]2) [p][trn]эк.[/p] закрывать; консервировать [com]([i]напр., транспортную линию, производство и т. п.[/i])[/com][/trn][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=1033]to abandon the transportation services[/lang] — заморозить транспортное обслуживание[/ex][/*][/m]
[m1]3) [p][trn]общ.[/p] оставлять, уходить [com]([i]с поста и т. д.[/i])[/com]; покидать, оставлять [com]([i]что-л. или кого-л.[/i])[/com][/trn][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=1033]to be forced to abandon a position[/lang] — быть вынужденным оставить должность[/ex][/*][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=1033]He abandoned his family and went abroad.[/lang] — Он оставил свою семью и поехал за границу.[/ex][/*][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=1033]He abandoned his car and tried to escape on foot.[/lang] — Он бросил машину и попытался ускользнуть пешком.[/ex][/*][/m]
[m2][*][b]See:[/b][/*][/m]
[m2][*][ref dict="Marketing (En-Ru)"]abandonment[/ref][/*][/m]
[b]2.[/b] [p]сущ.[/p]
[m1][p][trn]общ.[/p] импульсивность; развязанность, несдержанность[/trn][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=1033]to do smth. with in complete abandon[/lang] — делать что-л., совершенно забыв обо всем[/ex][/*][/m]
Show me abandon
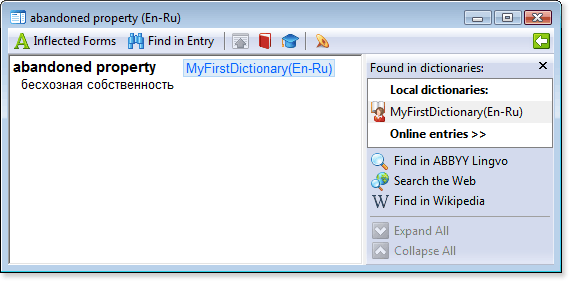
abandoned property
[m1][trn]бесхозная собственность[/trn][/m]
Show me abandoned property
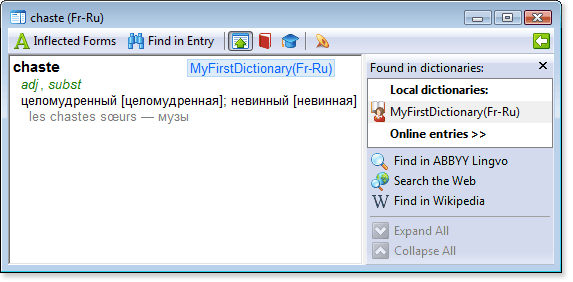
chaste
[m1][p][i][c][com]adj[/i][/p], [p][i]subst[/com][/c][/i][/p][/m]
[m1][trn]целом[']у[/']дренный \[целом[']у[/']дренная\]; нев[']и[/']нный \[нев[']и[/']нная\][/trn][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=1036]les chastes sœurs[/lang] — м[']у[/']зы[/ex][/*][/m]
Show me chaste
Qualität
[s]Qualität.wav[/s]
[m1][p][i][c][com]f[/p] [p]=[/i][/p], [lang id=32775]-en[/lang][/com][/c][/m]
[m1]1) [trn]качество, свойство[/trn][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=32775]Qualität I. \[erster\] Wahl[/lang] — качество первого сорта[/ex][/*][/m]
[m1]2) [trn]качество, достоинство[/trn][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=32775]er hat in der Stunde der Gefahr seine Qualitäten bewiesen[/lang] — в момент опасности он проявил свои достоинства \[свои лучшие качества\][/ex][/*][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=32775]ein Mann von Qualitäten[/lang] — человек с большими достоинствами[/ex][/*][/m]
[m1]3) [trn][com]([p][i]сокр.[/p] [lang id=32775]Q[/i])[/lang][/com] (высшее) качество; [p]ком.[/p] сорт[/trn][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=32775]beste Qualität[/lang] — высший сорт[/ex][/*][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=32775]diese Ware ist Qualität[/lang] — это товар высшего качества[/ex][/*][/m]
[m2][p][*][ex][lang id=32775]etw.[/p] auf die Qualität überprüfen[/lang] — проверить \[определить\] качество \[добротность\] [p]чего-л.[/ex][/*][/p][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=32775]von guter Qualität[/lang] — доброкачественный [com]([i]о товаре[/i])[/com][/ex][/*][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=32775]von schlechter Qualität[/lang] — недоброкачественный [com]([i]о товаре[/i])[/com][/ex][/*][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=32775]um hohe Qualität wetteifern[/lang] — бороться за высокое качество[/ex][/*][/m]
[m1]4) [trn]титул, звание, ранг[/trn][/m]
[m1]5) [trn]качество, уровень[/trn][/m]
[m2][*][ex][lang id=32775]erfinderische Qualität[/lang] — уровень изобретения[/ex][/*][/m]
[m1]6) [trn]класс [com]([i]машин[/i])[/com][/trn][/m]
[m1]7) [p][trn]фон.[/p] окраска, качество тембра [com]([i]гласного[/i])[/com][/trn][/m]
Show me Qualität
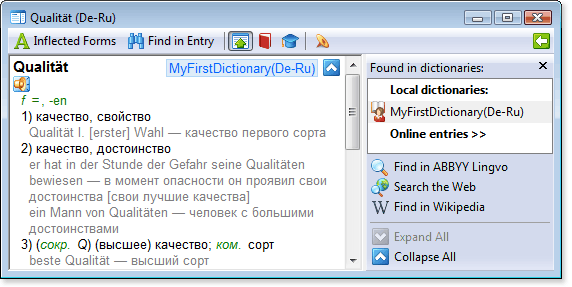
Note. To use these examples, please do the following:
- Copy the text of the entry (starting with the word in bold letters) into a text file. Make sure that each line in the entry body (but not the headword) starts with a tab.
- Add the dictionary header at the beginning of the file. The header
includes the dictionary name (#NAME “dictionary name”), the source
language (#INDEX_LANGUAGE “language name”), and the target language
(#CONTENTS_LANGUAGE “language name”).
E.g.: The following header at the beginning of the text file will create an English-Russian dictionary named “General”:
#NAME “General”
#INDEX_LANGUAGE “English”
#CONTENTS_LANGUAGE “Russian”
- Save the file as Unicode text and change its extension to *.dsl.
- Compile this file using DSL Compiler.




